Ventilation with heat recovery
Gain comfort & save energy

Fresh air in the house is essential - but regular ventilation often also means literally heating valuable heat out of the window. This can be avoided: A ventilation system with heat recovery ensures regular air exchange and at the same time prevents rooms from cooling down. In this way, you can increase your living comfort and the efficiency of your heating system - and thus also save on heating costs.
At a glance
- Regular ventilation helps to prevent mould and promotes well-being.
- Ventilation with heat recovery utilises heat from extract air to pleasantly preheat the incoming supply air.
- Advantages: Ventilation systems with heat recovery save heating costs, improve the indoor climate and increase living comfort.
- Installation options: Central ventilation unit with ventilation pipes into the rooms or decentralised pendulum fans in the outer wall of the respective room; both versions offer efficient heat recovery.
- Retrofitting during energy refurbishment: Controlled air exchange is particularly important with a tight building envelope. The principle of heat recovery increases the building's energy efficiency.
Why is ventilation important?
- Fresh air prevents oxygen deficiency and ensures well-being.
- Stale air, odours and moisture are transported outside.
- Regular air exchange helps to prevent mould and thus contributes to the protection of health and building fabric.
A problem with manual ventilation: In winter, heating warmth escapes through open windows - the rooms cool down and valuable energy is lost.
No more heating out the window
Ventilation with heat recovery
Residential ventilation systems replace the air without the need to open windows. In order to almost completely avoid heat loss through ventilation, many ventilation systems work with efficient heat recovery: the heat from the extract air is transferred to the fresh supply air so that it flows in at a pleasant temperature. Depending on the ventilation unit, around 90 per cent of the heat is recovered in this way. This saves heating costs and increases living comfort.
How heat recovery works in the ventilation unit
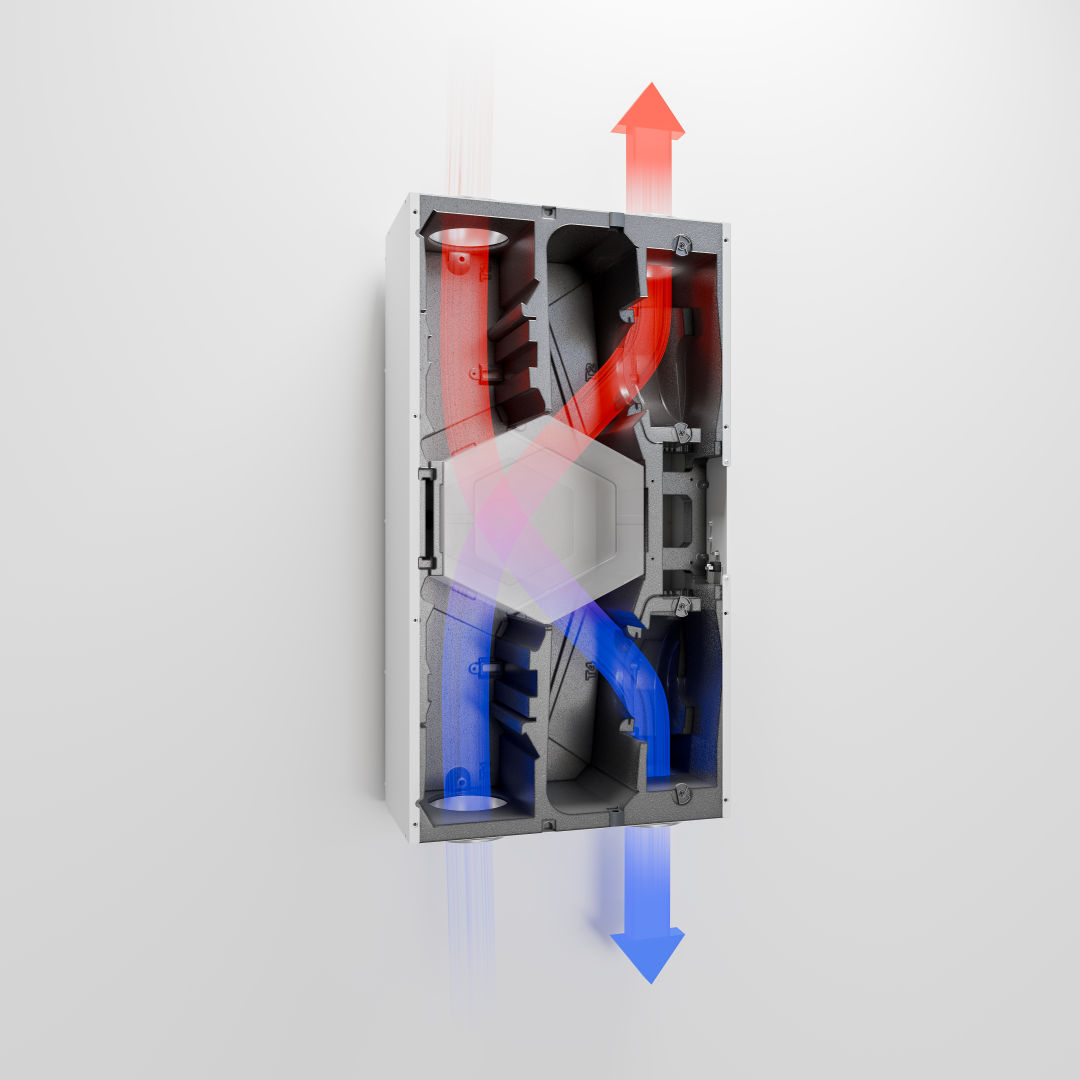
- The ventilation system extracts the stale, humid and warm air from the interior rooms to transport it outside.
- At the same time, fresh, cold outside air is drawn in and channelled into the rooms via the system.
- In an integrated heat exchanger, the system transfers the heat from the extract air to the incoming fresh air without the two airflows mixing.
- This preheating of the supply air significantly reduces the heating energy requirement.
- In this way, the system ensures continuous air exchange and minimises energy loss.
Tip for the summer
Bypass heat recovery
In summer, the rooms should remain cool, which is why pre-tempering of the incoming air by the extract air is not desirable. Modern ventilation systems therefore have a summer bypass that bypasses the heat exchanger and thus the heat recovery. This allows cool outside air to flow unhindered into the rooms, especially at night, and ensure pleasant temperatures.
Advantages of residental ventilation with heat recovery
- Energy saving: Residental ventilation with heat recovery saves energy and heating costs by recovering heat from the extract air and thus avoiding heat loss. This contributes to efficient and economical operation of the heating system.
- Better indoor climate and comfort: Ventilation with heat recovery ensures a better indoor climate and increases living comfort by continuously supplying fresh, clean air and regulating humidity. This eliminates the need for manual fans, keeps the room temperature constant and prevents draughts.
Further information about controlled residential ventilation can be found here.
Installation options for ventilation systems with heat recovery
Central ventilation system
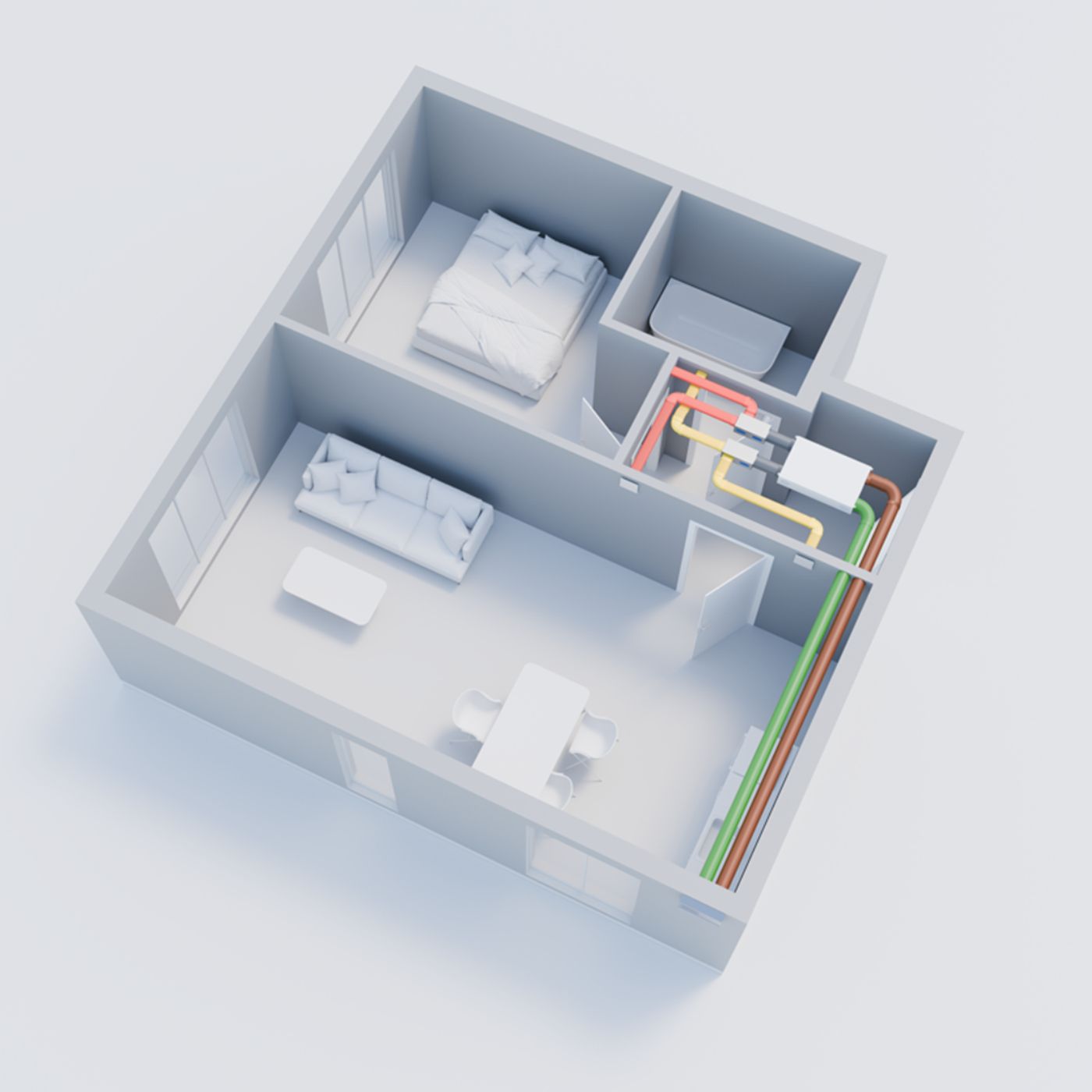
A centralised ventilation system consists of a central ventilation unit and ventilation pipes that supply the entire building with fresh air.
- Heat recovery takes place in the ventilation unit.
- Central ventilation systems achieve a high level of heat recovery and thus ensure efficient energy utilisation. Thanks to demand-led control, they also optimally adapt the air exchange to the actual demand.
- Installation: Ventilation ducts are usually laid in the screed or concrete in the building shell; however, they can also be installed retrospectively, e.g. in suspended ceilings. The central ventilation unit is usually located in the basement or plant room.
Decentralised ventilation system
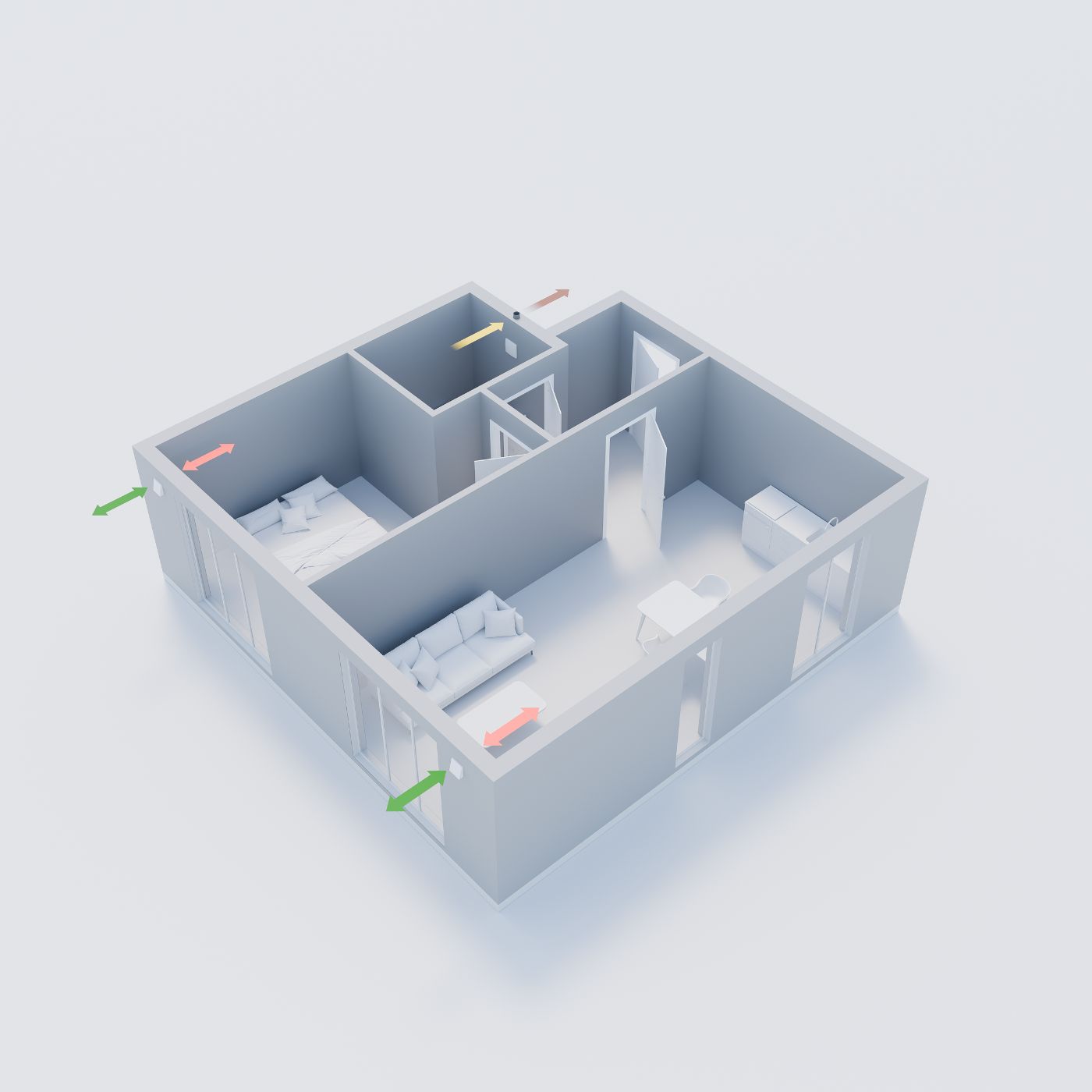
- Decentralised ventilation units are located directly in the outer wall of the respective rooms.
- So-called pendulum fans have an integrated heat exchanger that ensures efficient heat recovery.
- Installation: Decentralised ventilation units with heat recovery are simply installed in the outer wall using a special installation brick or core drilling. This also makes retrofitting particularly uncomplicated.
Tip: Filters in the residental ventilation system
Always fresh air without the rooms cooling down. This is a major advantage of a ventilation system with heat recovery. But did you know that residental ventilation can do even more? Equipped with highly efficient external filters, they also keep out dust, pollen and other pollutants. Allergy sufferers in particular can breathe a sigh of relief. Special filters can also reliably retain fine dust and the smallest particles. Important: To ensure the full effectiveness of the filters, regular filter changes are essential.
Retrofitting a ventilation system with heat recovery
Why this step makes sense for energy refurbishments
During energy refurbishments, the building envelope is carefully sealed to minimise heat loss. This greatly restricts the uncontrolled exchange of air, which increases the risk of mould growth. A ventilation system with heat recovery provides a remedy here by ensuring a controlled exchange of air. At the same time, it reduces the loss of valuable heating energy. It is therefore worth considering a ventilation solution that recovers heat efficiently when carrying out energy refurbishment and optimising the heating system.
Uncomplicated installation in energy-efficiently renovated old buildings
Centralised systems:
Flat ventilation units can be integrated into suspended ceilings, kitchen cabinets or pre-wall installations in the bathroom to save space. The associated ventilation pipes are usually installed in suspended ceilings so that the system works unobtrusively and efficiently.
Decentralised systems:
These systems are particularly suitable for retrofitting as they do not require complex pipe installations. The ventilation units are installed directly in the external wall by drilling a core hole.
FAQ
How does ventilation with heat recovery work?
A ventilation system with heat recovery extracts stale, warm air from indoor spaces and simultaneously supplies fresh air from outside. In a heat exchanger, the heat from the exhaust air is transferred to the fresh supply air without the air flows mixing. This preheats the incoming air, significantly reducing heating energy requirements.
What is the difference between centralised and decentralised ventilation with heat recovery?
In a central ventilation system, a central ventilation unit ensures air exchange throughout the entire building. To do this, it is connected to the individual rooms via ventilation pipes. In addition to a filter, the ventilation unit also has an integrated heat exchanger for efficient heat recovery. Decentralised ventilation units, on the other hand, are installed individually in the outer wall of each room and therefore do not require complex piping. Decentralised ventilation solutions with efficient heat recovery include pendulum fans, for example. Here, the heat exchanger is located directly in the respective fan.
What are the advantages of ventilation with heat recovery?
Whether with or without heat recovery, residential ventilation automatically exchanges the air in rooms, thereby preventing mould. Ventilation with heat recovery also uses the heat from the exhaust air to temper the supply air. This helps to save heating energy and improve the indoor climate by ensuring that the supply air is already at a comfortable temperature when it enters the room.
Can ventilation with heat recovery be combined with a heat pump?
Yes, ventilation with heat recovery can be combined with a heat pump. Thanks to the principle of heat recovery, residential ventilation even contributes to the efficiency of the entire heating system: during automatic air exchange, the heat from the exhaust air is used to preheat the incoming fresh air. This means that the valuable heat generated by the heat pump remains in the rooms and is not lost to the outside through ventilation. This reduces energy consumption and costs.